The Inaugural Launch Window is on April 17th, but may be subject to change judging by the road closures near Starbase at Bocca Chicca.
Finally, after Several tests of both Booster Seven and Starship Serial Number 24, Space rockets designer and manufacturer Space Exploration Technologies, AKA, SpaceX, is ready to launch Starship. This still depends very much on regulatory approvals from the United States Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), which has been keenly following the developments at Bocca Chica and South Padre Island, the next generation rocket build and test site, in Texas.
The fully stacked test rocket is now embraced by the Mechazilla chopsticks at Starbase in Boca Chica, Texas, USA, ready for the green light from the Federal Aviation Authority
What’s Starship?
SpaceX Starship is a next-generation spacecraft designed and built by SpaceX; the private space exploration company founded by billionaire inventor and entrepreneur Elon Musk. The Starship is a fully reusable spacecraft being developed to transport humans and cargo to the Earth’s Orbit, Moon, Asteroid belts, Mars, and other destinations in the solar system.
This next generation space rocket is composed of two parts: the Super Heavy rocket booster and the Starship spacecraft. The Super Heavy is a massive rocket booster providing the initial thrust to get the Starship off the ground, while the Starship is the spacecraft that will carry the crew and cargo to various destinations within the earth (point-to-point travel), earth’s orbit and other destinations in the solar system, and even beyond.
Starship is designed to be a fully reusable spacecraft, which means that both the Super Heavy booster and the Starship spacecraft can be used multiple times. This is expected to dramatically reduce the cost of spaceflight and enable humans to explore space more frequently and for longer periods of time.
The Rocket Manufacturer plans to use this next generation rocket to transport humans to the Moon as part of NASA’s Artemis program, which aims to establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon by 2024. SpaceX also plans to use the Starship to transport humans and cargo to Mars in the future, with the ultimate goal of establishing a self-sustaining human settlement on the Red Planet.
The Prototypes Testing Campaign
SpaceX has been conducting an extensive manufacturing and testing program of the Starship prototypes at their launch facility in Boca Chica, Texas. They have made several test flights of the Starship prototypes, with Serial Number 15, successfully landing back on the launch pad in October 2021 after reaching an altitude of 10 kilometers.
This launch is the next phase of testing, which should involve at least five orbital test flights of various Starship prototypes. The orbital test flights involve launching the Starships into Earth’s orbit, and then landing them back on Earth. This should be a significant milestone in the development of the Starship, as it would demonstrate the spacecraft’s ability to perform a controlled reentry and landing after a long-duration spaceflight.
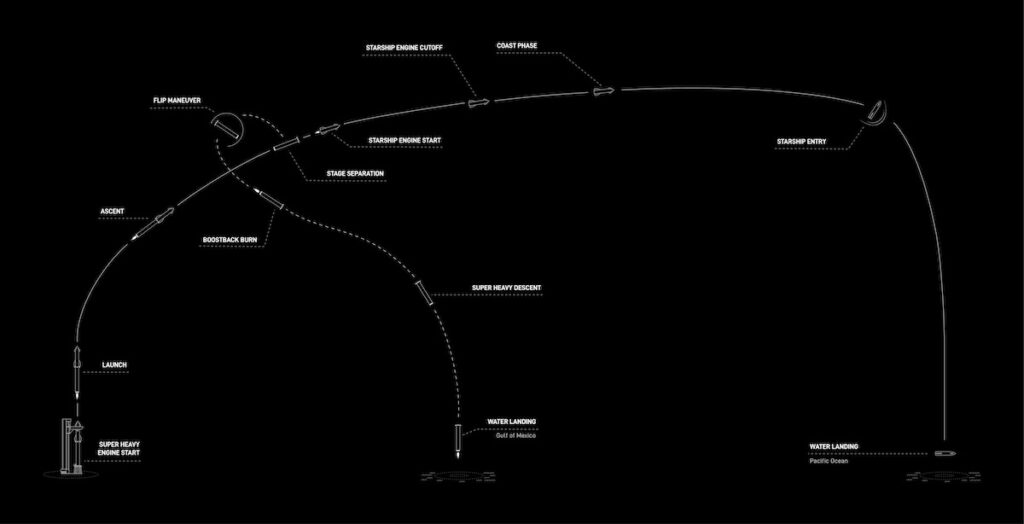
According to the latest Infographic on the SpaceX website however, Super Heavy Booster Seven is expected to Land back safely, being caught in the air by the robotic arms of the orbital launch Mount #OLM, while Starship Serial Number 24 is expected Splash on to the Atlantic Ocean, off the Gulf of Mexico.
The aim of this inaugural test flight is to get the accurate flight data for this biggest Space Rocket ever build, find weaknesses in the launch process and improve with subsequent manufacture, launches and orbital flights.
Next Orbital Flight tests should involve Super Heavy Booster Eight, Starship Serial Numbers 26, 27 and 28, which are being tested.

